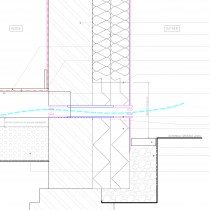
Detail for insulation to a ground floor and sub-floor, where the existing internal ground floor void is inaccessible, or it is not possible to lift the whole floor.
To allow the existing ground floor finish to be retained: a granular insulation infill is proposed to prevent heat loss through the floor, with perimeter insulation to footings, used to to prevent cold bridging through the external wall, and the ingress of damp and mould.
The sub-floor ventilation is used to ensure a reduced risk of condensation and humidity build up within the void, using a small humidity controlled fan. (This system can also be modified with temperature and humidity monitoring systems below the floor; as well as additional personal controls for the ventilation fan.)
View detail →