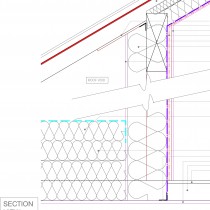
A roof insulation detail for the flanking wall of a room-in-roof or a storage space in roof, with additional loft insulation buildup as required to a minimum depth of 400mm to achieve the target U-value.
In this detail, insulation is installed to the upright stud walls between a room-in-roof and the loft space; along with insulation and membranes in plane of the existing rafters (where the existing roof membrane is non-breathable). It is important to ensure adequate ventilation over any insulation installed in the plane of the existing rafters.
In most cases, some loft insulation will already be installed (typically to a depth of between 50-200mm) in which case it is only required to add enough insulation to increase this to 400mm.
View detail →